Tool calling agent
Last updated Dec 4, 2025
In this example, we demonstrate how function calling (also known as tool calling) works with the Open AI API and Temporal. Tool calling allows the model to make decisions on which, if any, functions should be invoked. It also provides information to the LLM that will allow it to structure the response in such a way that the agent can easily invoke the functions.
Tools are supplied to the responses API through the tools parameter. The tools parameter is injson and includes a description of the function as well as descriptions of each of the arguments.
The API used to generate the tools json is an internal function from the Open AI API and may therefore change in the future. There currently is no public API to generate the tool definition from a Pydantic model or a function signature.
Being external API calls, invoking the LLM and invoking the function are each done within a Temporal Activity.
This example lays the foundation for the core agentic pattern where the LLM makes the decision on functions/tools to invoke, the agent calls the function/tool(s) and the response from such calls is sent back to the LLM for interpretation.
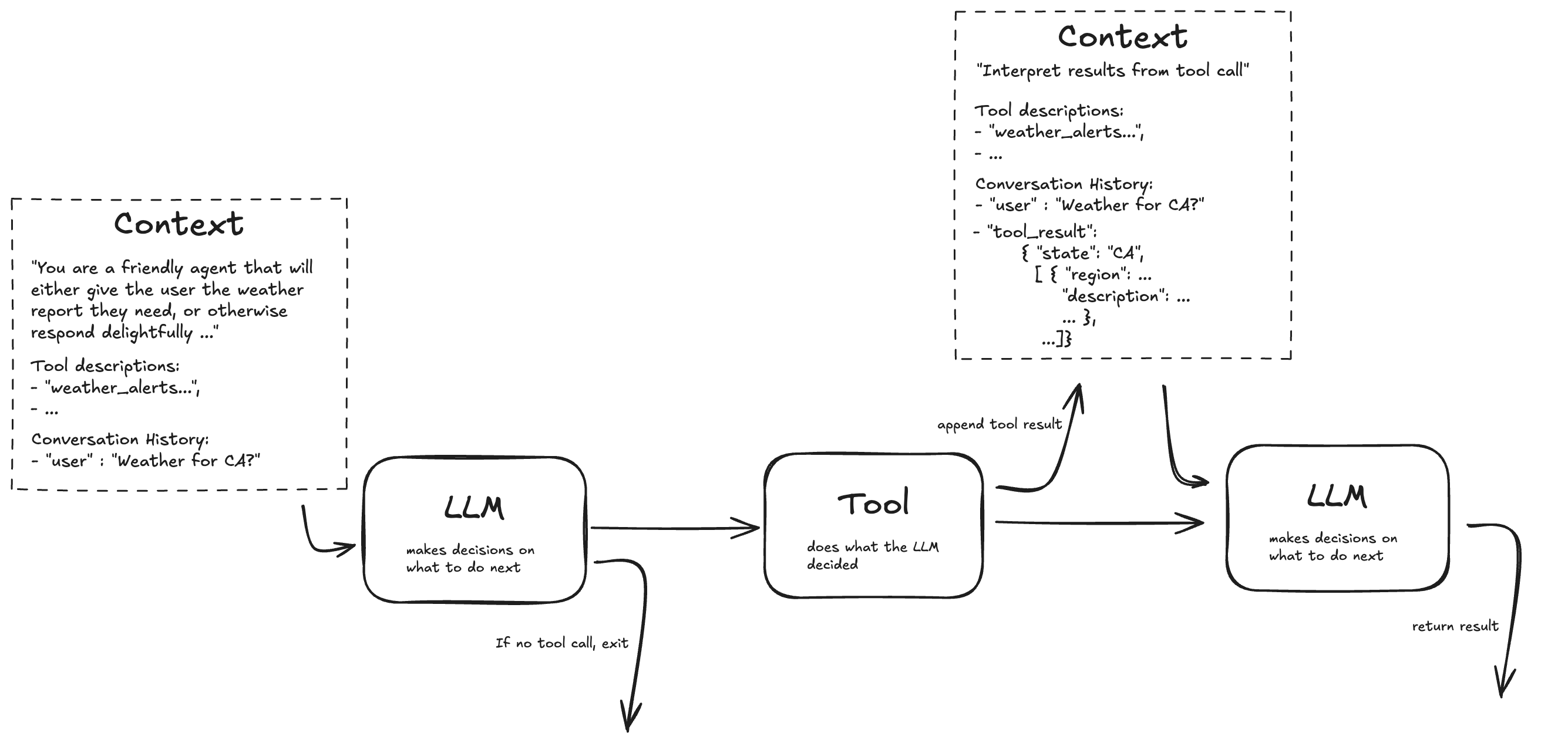
This recipe highlights these key design decisions:
- A generic Activity for invoking an LLM API; that is, instructions and other responses arguments are passed into the Activity making it appropriate for use in a variety of different use cases. Similarly, the result from the responses API call is returned out of the Activity so that it is usable in a variety of different use cases.
- We have intentionally not implemented the agentic loop so as to focus on how tool details are made available to the LLM and how functions are invoked. We do take the tool output and have the LLM interpret it in a manner consistent with the AI agent pattern.
- Retries are handled by Temporal and not by the underlying libraries such as the OpenAI client. This is important because if you leave the client retries on they can interfere with correct and durable error handling and recovery.
Create the Activity for LLM invocations
We create a wrapper for the create method of the AsyncOpenAI client object.
This is a generic Activity that invokes the OpenAI LLM.
We set max_retries=0 when creating the AsyncOpenAI client.
This moves the responsibility for retries from the OpenAI client to Temporal.
In this implementation, we allow for the model, instructions and input to be passed in, and also the list of tools.
activities/openai_responses.py
from temporalio import activity
from openai import AsyncOpenAI
from openai.types.responses import Response
from dataclasses import dataclass
from typing import Any
# Temporal best practice: Create a data structure to hold the request parameters.
@dataclass
class OpenAIResponsesRequest:
model: str
instructions: str
input: object
tools: list[dict[str, Any]]
@activity.defn
async def create(request: OpenAIResponsesRequest) -> Response:
# Temporal best practice: Disable retry logic in OpenAI API client library.
client = AsyncOpenAI(max_retries=0)
resp = await client.responses.create(
model=request.model,
instructions=request.instructions,
input=request.input,
tools=request.tools,
timeout=30,
)
return resp
Create the Activity for the tool invocation
We create a wrapper for invoking the National Weather Service API, specifically for the weather alerts endpoint.
We follow the Temporal best practice of encapsulating all input parameters to the activity in data structure, even here where this is only one argument.
The WEATHER_ALERTS_TOOL_OAI leverages a function defined in helpers/tool_helpers.py that calls the aforementioned internal OpenAI function, generating a dictionary that becomes the argument passed into the OpenAI responses API.
activities/get_weather_alerts.py
# weather_activities.py
from typing import Any
from temporalio import activity
import httpx
import json
from pydantic import BaseModel
import openai
from helpers import tool_helpers
from pydantic import Field
# Constants
NWS_API_BASE = "https://api.weather.gov"
USER_AGENT = "weather-app/1.0"
def _alerts_url(state: str) -> str:
return f"{NWS_API_BASE}/alerts/active/area/{state}"
# External calls happen via activities now
async def _make_nws_request(url: str) -> dict[str, Any] | None:
"""Make a request to the NWS API with proper error handling."""
headers = {
"User-Agent": USER_AGENT,
"Accept": "application/geo+json"
}
async with httpx.AsyncClient() as client:
response = await client.get(url, headers=headers, timeout=5.0)
response.raise_for_status()
return response.json()
# Build the tool for the OpenAI Responses API. We use Pydantic to create a structure
# that encapsulates the input parameters for both the weather alerts activity and the
# tool definition that is passed to the OpenAI Responses API.
class GetWeatherAlertsRequest(BaseModel):
state: str = Field(description="Two-letter US state code (e.g. CA, NY)")
WEATHER_ALERTS_TOOL_OAI: dict[str, Any] = tool_helpers.oai_responses_tool_from_model(
"get_weather_alerts",
"Get weather alerts for a US state.",
GetWeatherAlertsRequest)
@activity.defn
async def get_weather_alerts(weather_alerts_request: GetWeatherAlertsRequest) -> str:
"""Get weather alerts for a US state.
Args:
state: Two-letter US state code (e.g. CA, NY)
"""
data = await _make_nws_request(_alerts_url(weather_alerts_request.state))
return json.dumps(data)
Create the helper function
The oai_responses_tool_from_model function accepts a tool name and description, as well as a list of argument name/description pairs and returns json that is in the format expected for tool definitions in the OpenAI responses API.
The API used to generate the tools json is an interal function from the Open AI API and may therefore change in the future. There currently is no public API to generate the tool definition from a Pydantic model or a function signature.
helpers/tool_helpers.py
from openai.lib._pydantic import to_strict_json_schema # private API; may change
# there currently is no public API to generate the tool definition from a Pydantic model
# or a function signature.
from pydantic import BaseModel
def oai_responses_tool_from_model(name: str, description: str, model: type[BaseModel]):
return {
"type": "function",
"name": name,
"description": description,
"parameters": to_strict_json_schema(model),
"strict": True,
}
Create the Agent
The agent is implemented as a Temporal workflow that orchestrates
- the intial LLM call with the initial user input and guidance to the LLM that they should respond in haiku when the user input doesn't lead to a tool call,
- the invocation of the function, if the LLM has chosen one
- and if a function has been called, the result is appended to the context that is then sent back to the LLM for interpretation (the LLM is instructed to format the tool response).
workflows/get_weather_workflow.py
from temporalio import workflow
from datetime import timedelta
import json
from activities import openai_responses
with workflow.unsafe.imports_passed_through():
from activities import get_weather_alerts
@workflow.defn
class ToolCallingWorkflow:
@workflow.run
async def run(self, input: str) -> str:
input_list = [ {"role": "user", "content": input} ]
# We take the user input and pass it to the LLM with the system instructions
# and the tool to use, if applicable.
system_instructions = "if no tools seem to be needed, respond in haikus."
result = await workflow.execute_activity(
openai_responses.create,
openai_responses.OpenAIResponsesRequest(
model="gpt-4o-mini",
instructions=system_instructions,
input=input_list,
tools=[get_weather_alerts.WEATHER_ALERTS_TOOL_OAI],
),
start_to_close_timeout=timedelta(seconds=30),
)
# For this simple example, we only have one item in the output list
item = result.output[0]
# if the result is a tool call, call the tool
if item.type == "function_call":
if item.name == "get_weather_alerts":
# serialize the output, which is an OpenAI object
input_list += [
i.model_dump() if hasattr(i, "model_dump") else i
for i in result.output
]
result = await workflow.execute_activity(
get_weather_alerts.get_weather_alerts,
get_weather_alerts.GetWeatherAlertsRequest(state=json.loads(item.arguments)["state"]),
start_to_close_timeout=timedelta(seconds=30),
)
# add the tool call result to the input list for context
input_list.append({"type": "function_call_output",
"call_id": item.call_id,
"output": result})
result = await workflow.execute_activity(
openai_responses.create,
openai_responses.OpenAIResponsesRequest(
model="gpt-4o-mini",
instructions="return the tool call result in a readable format",
input=input_list,
tools=[]
),
start_to_close_timeout=timedelta(seconds=30),
)
result = result.output_text
return result
Create the Worker
The worker is the process that dispatches work to the various parts of the agent implementation - the orchestrator and the activities for the LLM and tool invocations.
File: worker.py
import asyncio
from temporalio.client import Client
from temporalio.worker import Worker
from workflows.get_weather_workflow import ToolCallingWorkflow
from activities import openai_responses, get_weather_alerts
from temporalio.contrib.pydantic import pydantic_data_converter
async def main():
client = await Client.connect(
"localhost:7233",
data_converter=pydantic_data_converter,
)
worker = Worker(
client,
task_queue="tool-calling-python-task-queue",
workflows=[
ToolCallingWorkflow,
],
activities=[
openai_responses.create,
get_weather_alerts.get_weather_alerts,
],
)
await worker.run()
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(main())
Initiate an interaction with the agent
In order to interact with this simple AI agent, we create a Temporal client and execute a workflow.
start_workflow.py
import asyncio
import sys
from temporalio.client import Client
from workflows.get_weather_workflow import ToolCallingWorkflow
from temporalio.contrib.pydantic import pydantic_data_converter
async def main():
client = await Client.connect(
"localhost:7233",
data_converter=pydantic_data_converter,
)
query = sys.argv[1] if len(sys.argv) > 1 else "Hello, how are you?"
# Submit the Tool Calling workflow for execution
result = await client.execute_workflow(
ToolCallingWorkflow.run,
query,
id="my-workflow-id",
task_queue="tool-calling-python-task-queue",
)
print(f"Result: {result}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(main())
Running
Start the Temporal Dev Server
temporal server start-dev
Install dependencies
From this directory:
uv sync
Run the worker
First set the OPENAI_API_KEY environment variable and then:
uv run python -m worker
Initiate an interaction with the agent
This user input should not result in any tool call
uv run python -m start_workflow "Tell me about recursion in programming."
This user input should invoke the tool and respond with current weather alerts for California.
uv run python -m start_workflow "Are there any weather alerts in California?"