Develop code that durably executes - Java SDK dev guide
When it comes to the Temporal Platform's ability to durably execute code, the SDK's ability to Replay a Workflow Execution is a major aspect of that. This chapter introduces the development patterns which enable that.
This chapter of the Temporal Java SDK developer's guide introduces best practices to developing deterministic Workflows that can be Replayed, enabling a Durable Execution.
By the end of this section you will know basic best practices for Workflow Definition development.
Learning objectives:
- Identify SDK API calls that map to Events
- Recognize non-deterministic Workflow code
- Explain how Workflow code execution progresses
The information in this chapter is also available in the Temporal 102 course.
This chapter builds on the Construct a new Temporal Application project chapter and relies on the Background Check use case and sample applications as a means to contextualize the information.
This chapter walks through the following sequence:
- Retrieve a Workflow Execution's Event History
- Add a Replay test to your application
- Intrinsic non-deterministic logic
- Non-deterministic code changes
Retrieve a Workflow Execution's Event History
There are a few ways to view and download a Workflow Execution's Event History. We recommend starting off by using either the Temporal CLI or the Web UI to access it.
Using the Temporal CLI
Use the Temporal CLI's temporal workflow show command to save your Workflow Execution's Event History to a local file.
Run the command from the /backgroundcheckreplay directory so that the file is available to the testing files.
/backgroundcheck
...
/main
/test
backgroundcheck_workflow_history.json
Local dev server
If you have been following along with the earlier chapters of this guide, your Workflow Id might be something like backgroundcheck_workflow.
temporal workflow show \
--workflow-id backgroundcheck_workflow \
--output json > backgroundcheck_workflow_event_history.json
The most recent Event History for that Workflow Id is returned when you only use the Workflow Id to identify the Workflow Execution.
Use the --run-id option as well to get the Event History of an earlier Workflow Execution by the same Workflow Id.
Temporal Cloud
For Temporal Cloud, remember to either provide the paths to your certificate and private keys as command options, or set those paths as environment variables:
temporal workflow show \
--workflow-id backgroundcheck_workflow \
--namespace backgroundcheck_namespace \
--tls-cert-path /path/to/ca.pem \
--tls-key-path /path/to/ca.key \
--output json > backgroundcheck_workflow_history.json
Self-hosted Temporal Cluster
For self-hosted environments, you might be using the Temporal CLI command alias:
temporal_docker workflow show \
--workflow-id backgroundcheck_workflow \
--namespace backgroundcheck_namespace \
--output json > backgroundcheck_workflow_history.json
Via the UI
A Workflow Execution's Event History is also available in the Web UI.
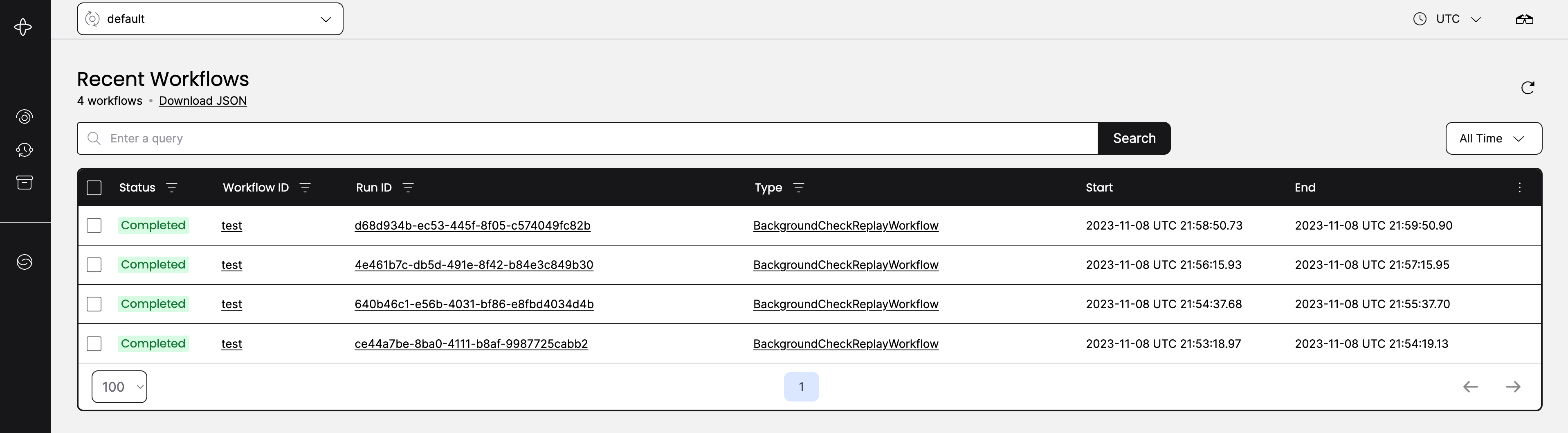
Navigate to the Workflows page in the UI and select the Workflow Execution.
Select a Workflow Execution from the Workflows page
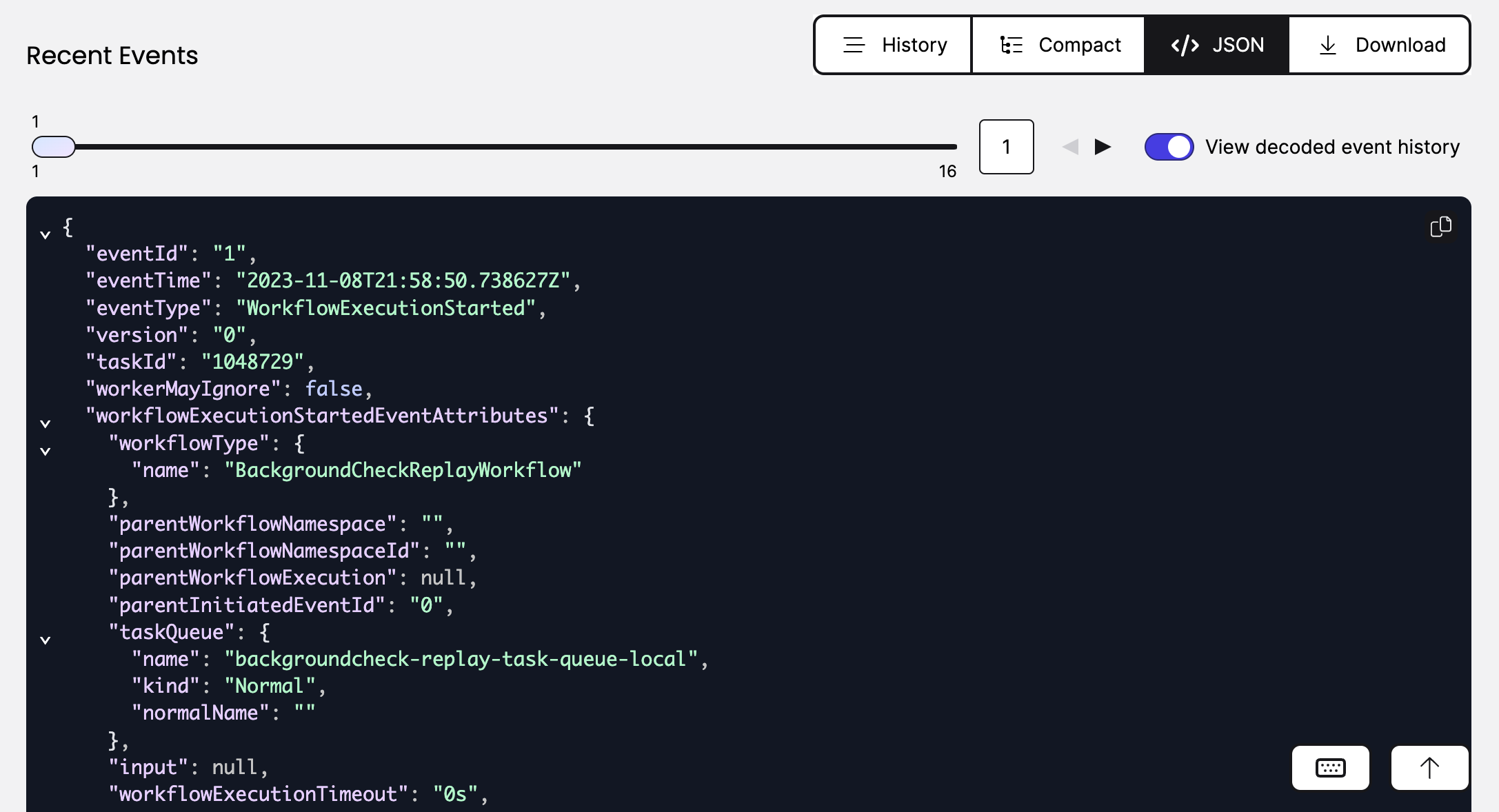
From the Workflow details page you can copy the Event History from the JSON tab and paste it into the backgroundcheck_workflow_history.json file.
Copy Event History JSON object from the Web UI
Add a Replay test
View the source code
in the context of the rest of the application code.
@Test
public void testSuccessfulReplayFromFile(TestWorkflowEnvironment testEnv, Worker worker,
BackgroundCheckReplayWorkflow workflow) throws Exception {
File eventHistoryFile = new File("backgroundcheck_workflow_event_history.json");
assertDoesNotThrow(() -> WorkflowReplayer.replayWorkflowExecution(eventHistoryFile,
BackgroundCheckReplayWorkflowImpl.class));
}
Why add a Replay test?
The Replay test is important because it verifies whether the current Workflow code (Workflow Definition) remains compatible with the Event Histories of earlier Workflow Executions.
A failed Replay test typically indicates that the Workflow code exhibits non-deterministic behavior. In other words, for a specific input, the Workflow code can follow different code paths during each execution, resulting in distinct sequences of Events. The Temporal Platform's ability to ensure durable execution depends on the SDK's capability to re-execute code and return to the most recent state of the Workflow Function execution.
The Replay test executes the same steps as the SDK and verifies compatibility.
Workflow code becomes non-deterministic primarily through two main avenues:
- Intrinsic non-deterministic logic: This occurs when Workflow state or branching logic within the Workflow gets determined by factors beyond the SDK's control.
- Non-deterministic code changes: When you change your Workflow code and deploy those changes while there are still active Workflow Executions relying on older code versions.
Intrinsic non-deterministic logic
Referred to as "intrinsic non-determinism" this kind of "bad" Workflow code can prevent the Workflow code from completing because the Workflow can take a different code path than the one expected from the Event History.
The following are some common operations that can't be done inside of a Workflow Definition:
- Generate and rely on random numbers (Use Activites instead).
- Accessing / mutating external systems or state. This includes calling an external API, conducting a file I/O operation, talking to another service, etc. (use Activities instead).
- Relying on system time.
- Use
Workflow.currentTimeMillis()as a replacement forSystem.CurrentTimeMillis(). - Use
Workflow.Sleep()as a replacement forThread.Sleep().
- Use
- Working directly with threads.
- Iterating over data structures with unknown ordering.
This includes iterating over HashMaps using
foras the order is randomized. Instead you can collect the keys of the map, sort them, and then iterate over the sorted keys to access the map or consider using aLinkedHashMapor other ordered data structure. This technique provides deterministic results. - Storing or evaluating the run Id.
One way to produce a non-deterministic error is to use a random number to determine whether to sleep inside the Workflow.
View the source code
in the context of the rest of the application code.
import io.temporal.activity.ActivityOptions;
import io.temporal.workflow.Workflow;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import java.time.Duration;
import java.util.Random;
public class BackgroundCheckReplayNonDeterministicWorkflowImpl implements BackgroundCheckReplayNonDeterministicWorkflow {
// Define the Activity Execution options
// StartToCloseTimeout or ScheduleToCloseTimeout must be set
ActivityOptions options = ActivityOptions.newBuilder()
.setStartToCloseTimeout(Duration.ofSeconds(5))
.build();
// Create an client stub to activities that implement the given interface
private final BackgroundCheckReplayActivities activities =
Workflow.newActivityStub(BackgroundCheckReplayActivities.class, options);
@Override
public String backgroundCheck(String socialSecurityNumber) {
// CAUTION, the following code is an anti-pattern showing what NOT to do
Random random = new Random();
if(random.nextInt(101)>= 50){
Workflow.sleep(Duration.ofSeconds(60));
}
// Execute the Activity synchronously (wait for the result before proceeding)
String ssnTraceResult = activities.ssnTraceActivity(socialSecurityNumber);
// Make the results of the Workflow available
return ssnTraceResult;
}
}
Non-deterministic code changes
The most important thing to take away from the section is to make sure you have an application versioning plan whenever you are developing and maintaining a Temporal Application that will eventually deploy to a production environment.
Versioning APIs and versioning strategies are covered in other parts of the developer's guide, this chapter sets the stage to understand why and how to approach those strategies.
The Event History
Inspect the Event History of a recent Background Check Workflow using the temporal workflow show command:
temporal workflow show \
--workflow-id backgroundcheck_workflow \
--namespace backgroundcheck_namespace
You should see output similar to this:
Progress:
ID Time Type
1 2023-11-08T21:58:50Z WorkflowExecutionStarted
2 2023-11-08T21:58:50Z WorkflowTaskScheduled
3 2023-11-08T21:58:50Z WorkflowTaskStarted
4 2023-11-08T21:58:50Z WorkflowTaskCompleted
5 2023-11-08T21:58:50Z TimerStarted
6 2023-11-08T21:59:50Z TimerFired
7 2023-11-08T21:59:50Z WorkflowTaskScheduled
8 2023-11-08T21:59:50Z WorkflowTaskStarted
9 2023-11-08T21:59:50Z WorkflowTaskCompleted
10 2023-11-08T21:59:50Z ActivityTaskScheduled
11 2023-11-08T21:59:50Z ActivityTaskStarted
12 2023-11-08T21:59:50Z ActivityTaskCompleted
13 2023-11-08T21:59:50Z WorkflowTaskScheduled
14 2023-11-08T21:59:50Z WorkflowTaskStarted
15 2023-11-08T21:59:50Z WorkflowTaskCompleted
16 2023-11-08T21:59:50Z WorkflowExecutionCompleted
Result:
Status: COMPLETED
Output: ["pass"]
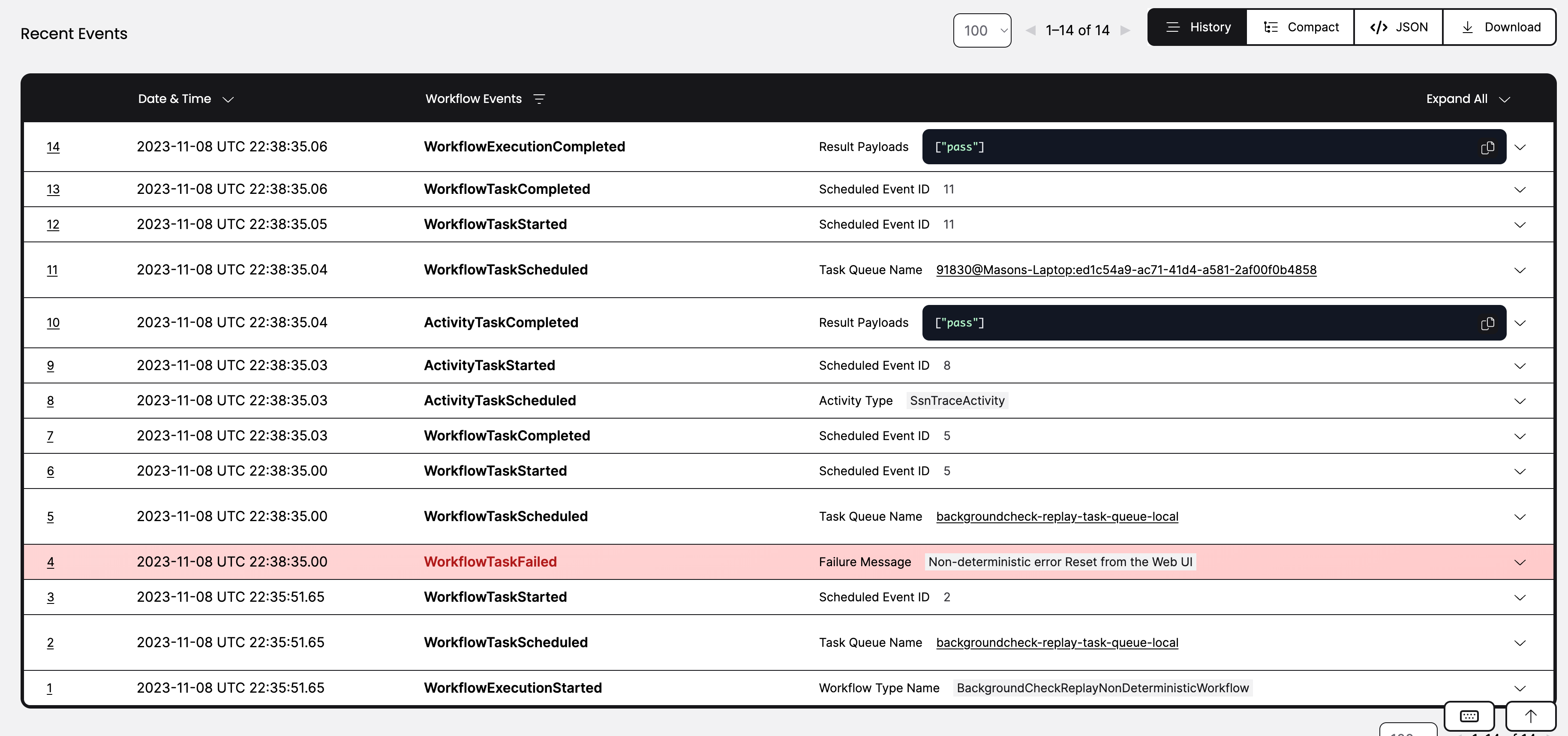
The preceding output shows eleven Events in the Event History ordered in a particular sequence. All Events are created by the Temporal Server in response to either a request coming from a Temporal Client, or a Command coming from the Worker.
Let's take a closer look:
WorkflowExecutionStarted: This Event is created in response to the request to start the Workflow Execution.WorkflowTaskScheduled: This Event indicates a Workflow Task is in the Task Queue.WorkflowTaskStarted: This Event indicates that a Worker successfully polled the Task and started evaluating Workflow code.WorkflowTaskCompleted: This Event indicates that the Worker suspended execution and made as much progress that it could.TimerStarted: This Event schedules a durable timer and records it in the Event History.TimerFired: After the time specified in the Timer has passed, the Timer fires, resuming execution.WorkflowTaskScheduled: The Workflow resumes progress and records aWorkflowTaskScheduledevent to drive progress forward.WorkflowTaskStarted: The Workflow will continue executing when an available Worker polls the Temporal Cluster and picks up the task to be executed. Once the Worker has begun it issues aWorkflowTaskStartedcommand to the cluster.WorkflowTaskCompleted: The Workflow progresses until it reaches a line that issues a Command to the Temporal Cluster. The Workflow suspends execution as it made as much progress as it could.ActivityTaskScheduled: This Event indicates that a request to execute an Activity was made, in this instance a call to theSSNTraceActivity, and the Worker sent theScheduleActivityTaskCommand to the Server.ActivityTaskStarted: This Event indicates that the Worker successfully polled the Activity Task and started evaluating Activity code.ActivityTaskCompleted: This Event indicates that the Worker completed evaluation of the Activity code and returned any results to the Server. In response, the Server schedules another Workflow Task to finish evaluating the Workflow code resulting in the remaining Events,WorkflowTaskScheduled.WorkflowTaskStarted,WorkflowTaskCompleted,WorkflowExecutionCompleted.
The Event reference serves as a source of truth for all possible Events in the Workflow Execution's Event History and the data that is stored in them.
Add a call to sleep
In the following sample, we add a couple of logging statements and a Timer to the Workflow code to see how this affects the Event History.
Use the Workflow.sleep API to reqest the Workflow to sleep for a minute before the call to execute the Activity.
The Temporal SDK offers both a Workflow.newTimer() API, and a Workflow.sleep() API that enables you to add time based logic to your Workflow code.
Use the Workflow.getLogger API to log from Workflows to suppress repeated logs from the Replay of the Workflow code.
View the source code
in the context of the rest of the application code.
package backgroundcheckreplay;
import io.temporal.activity.ActivityOptions;
import io.temporal.workflow.Workflow;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import java.time.Duration;
public class BackgroundCheckReplayWorkflowImpl implements BackgroundCheckReplayWorkflow {
public static final Logger logger = Workflow.getLogger(BackgroundCheckReplayWorkflowImpl.class);
// Define the Activity Execution options
// StartToCloseTimeout or ScheduleToCloseTimeout must be set
ActivityOptions options = ActivityOptions.newBuilder()
.setStartToCloseTimeout(Duration.ofSeconds(5))
.build();
// Create an client stub to activities that implement the given interface
private final BackgroundCheckReplayActivities activities =
Workflow.newActivityStub(BackgroundCheckReplayActivities.class, options);
@Override
public String backgroundCheck(String socialSecurityNumber) {
// Sleep for 1 minute
logger.info("Sleeping for 1 minute...");
Workflow.sleep(Duration.ofSeconds(60));
logger.info("Finished sleeping");
// Execute the Activity synchronously (wait for the result before proceeding)
String ssnTraceResult = activities.ssnTraceActivity(socialSecurityNumber);
// Make the results of the Workflow available
return ssnTraceResult;
}
}
Inspect the new Event History
After updating your Workflow code to include the logging and Timer, run your tests again.
You should expect to see the TestReplayWorkflowHistoryFromFile test fail.
This is because the code we added creates new Events and alters the Event History sequence.
To get this test to pass, we must get an updated Event History JSON file. Start a new Workflow and after it is complete download the Event History as a JSON object.
Reminder that this guide jumps between several sample applications using multiple Task Queues. Make sure you are starting Workflows on the same Task Queue that the Worker is listening to. And, always make sure that all Workers listening to the same Task Queue are registered with the same Workflows and Activities.
If you inspect the new Event History, you will see two new Events in response to the Workflow.sleep() API call which send the StartTimer Command to the Server:
TimerStartedTimerFired
However, it is also important to note that you don't see any Events related to logging. And if you were to remove the Sleep call from the code, there wouldn't be a compatibility issue with the previous code. This is to highlight that only certain code changes within Workflow code is non-deterministic. The basic thing to remember is that if the API call causes a Command to create Events in the Workflow History that takes a new path from the existing Event History then it is a non-deterministic change.
This becomes a critical aspect of Workflow development when there are running Workflows that have not yet completed and rely on earlier versions of the code.
Practically, that means non-deterministic changes include but are not limited to the following:
- Adding or removing an Activity
- Adding or removing a Timer
- Altering the execution order of Activities or Timers relative to one another
The following are a few examples of changes that do not lead to non-deterministic errors:
- Modifying non-Command generating statements in a Workflow Definition, such as logging statements
- Changing attributes in the
ActivityOptions - Modifying code inside of an Activity Definition
Workflow Reset
One way of fixing a Workflow that is blocked by a non-deterministic error is to reset the Workflow to an earlier state and allowing it to progress. However, this will only work if you have removed the source of the non-deterministic error. Also, resetting a Workflow to a certain state will discard any progress the Workflow may have made after that point, so be certain this is the action you wish to take.
Resetting via the Web UI
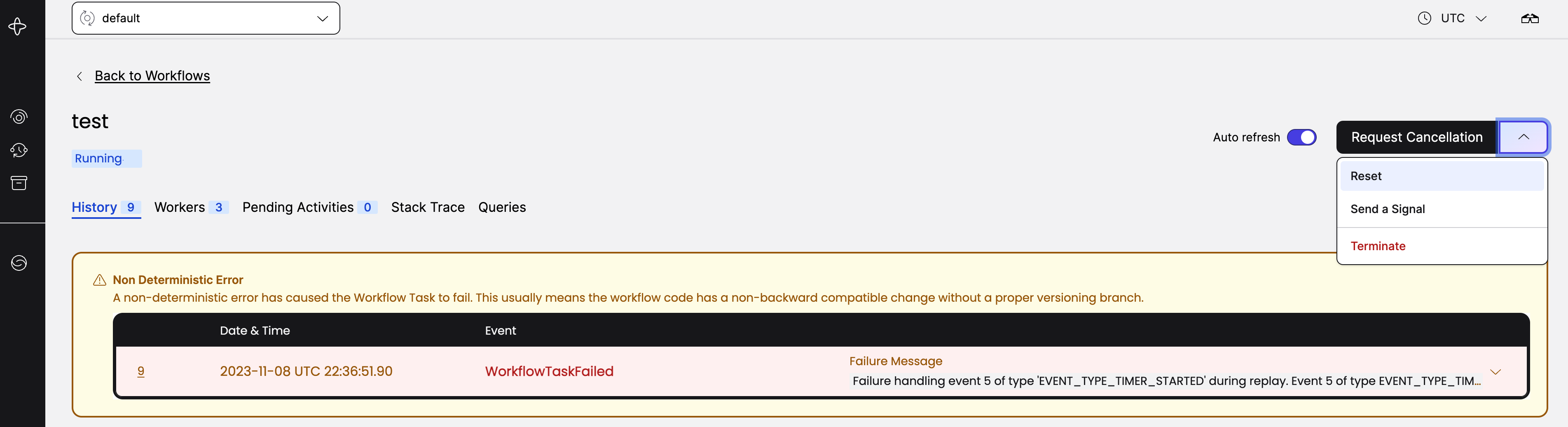
Let's say you decided you don't need the Timer in this current Workflow and decided to delete it. Once you have deployed your change, you would go to the currently blocked Workflow in the Web-UI and select Reset from the dropdown in the top right.
Select the Workflow Reset Option
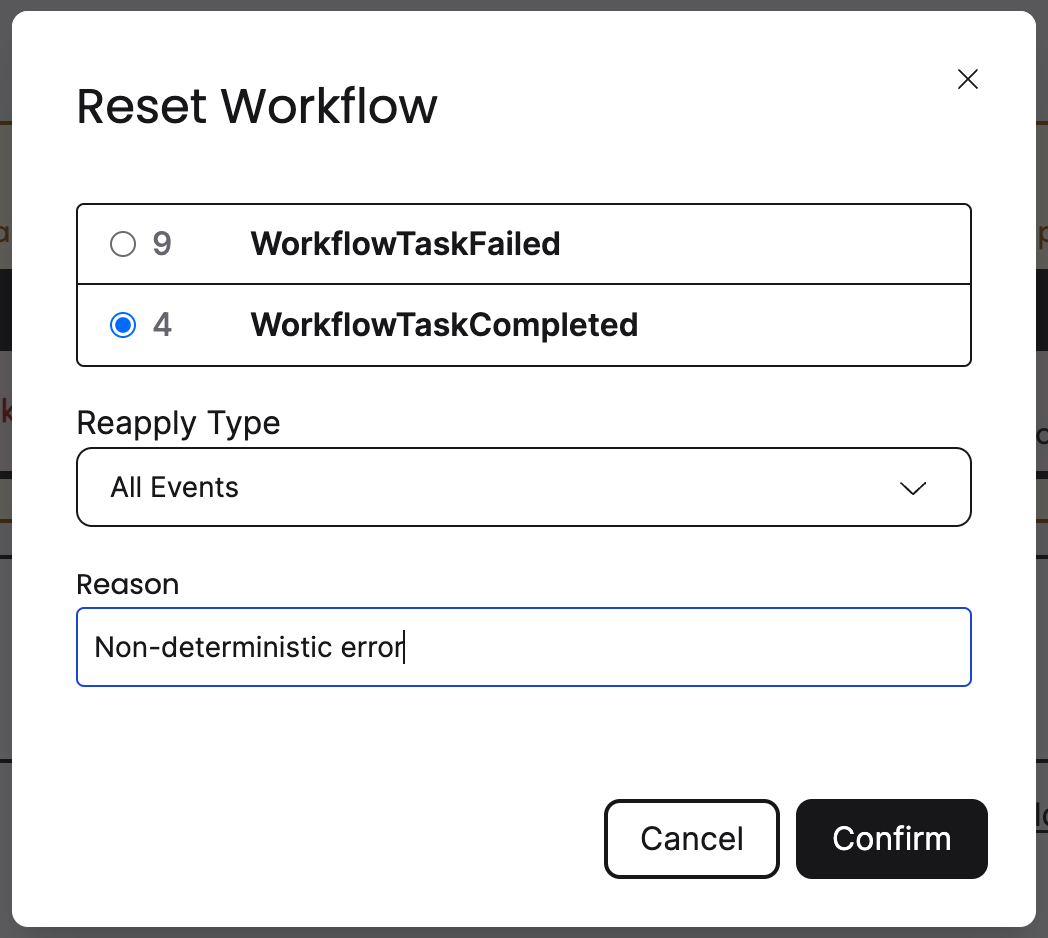
Next you'll see a list of available points where the Workflow can be reset to.
The only valid option would be to reset the Worklfow to the first WorkflowTaskCompleted
with event ID 4 as it is before the WorkflowTaskFailed event. You should also
always include a reason why you are resetting this event. The reason will be
persisted in the Event History and may be useful to others who inspect why the
Workflow was reset.
Workflow Reset Points
Once you've reset the Workflow you'll notice that the Workflow terminated and the Web UI provided a link to a new Workflow execution. The Event History up until the point you chose was copied over and executed.
Workflow Terminated and Reset
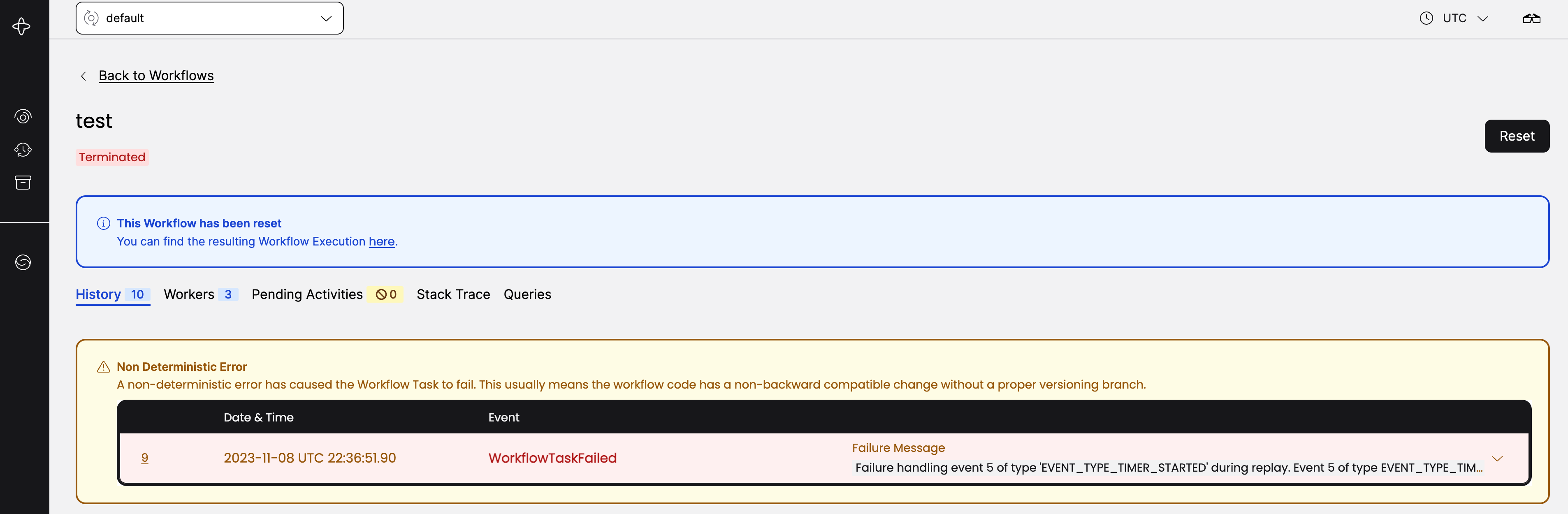
After the Timer has fired the Workflow should execute to completion without any
more errors. If you scroll down in the Web UI you'll see the new Event History,
including the WorkflowTaskFailed event that was used as the reset point, along
with the reason you reset the workflow.
New Event History Success with Reset
Resetting via the CLI
The following temporal command is the equivalent of doing it in the Web UI
$ temporal workflow reset \
--workflow-id my-workflow-id \
--event-id 4 \
--reason "Non-deterministic Error"
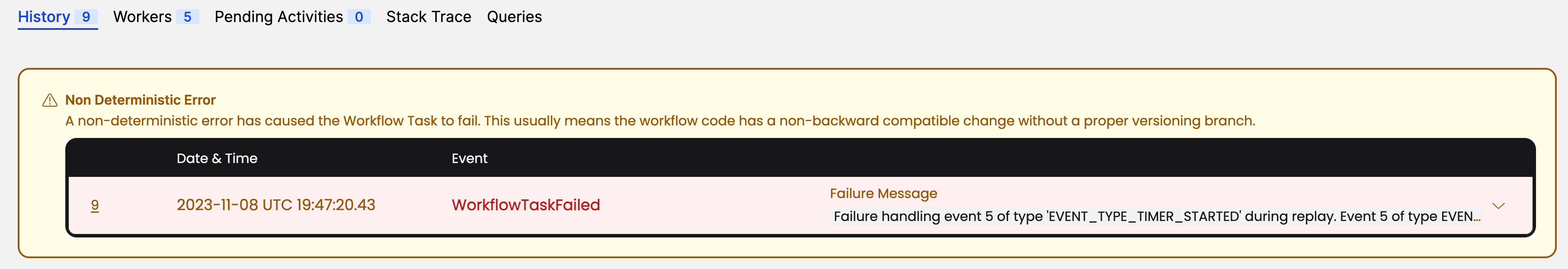
If you run the BackgroundCheckReplayNonDeterministicWorkflow Workflow enough times, eventually you will see a Workflow Task failure.
The Worker logs will show something similar to the following:
13:47:20.429 WARN - Workflow task processing failure. startedEventId=8, WorkflowId=test, RunId=20ec9811-89c5-454e-b9ed-c284f19565e4. If seen continuously the workflow might be stuck.
io.temporal.worker.NonDeterministicException: Failure handling event 5 of type 'EVENT_TYPE_TIMER_STARTED' during replay. Event 5 of type EVENT_TYPE_TIMER_STARTED does not match command type COMMAND_TYPE_SCHEDULE_ACTIVITY_TASK. {WorkflowTaskStartedEventId=8, CurrentStartedEventId=3}
at io.temporal.internal.statemachines.WorkflowStateMachines.handleCommandEvent(WorkflowStateMachines.java:442)
...
And you will see information about the failure in the Web UI as well.
Web UI view of a non-determinism error
To inspect the Workflow Task failure using the Temporal CLI, you can use the long value for the --fields command option with the temporal workflow show command.
temporal workflow show \
--workflow-id backgroundcheck_workflow_break \
--namespace backgroundcheck_namespace \
--fields long
This will display output similar to the following:
Progress:
[95mID[0m [95m Time [0m [95m Type [0m [95m Details [0m
1 2023-11-08T19:46:20Z WorkflowExecutionStarted {WorkflowType:{Name:BackgroundCheckReplayNonDeterministicWorkflow},
ParentInitiatedEventId:0,
TaskQueue:{Name:backgroundcheck-replay-task-queue-local,
Kind:Normal}, WorkflowExecutionTimeout:0s, WorkflowRunTimeout:0s,
WorkflowTaskTimeout:10s, Initiator:Unspecified,
OriginalExecutionRunId:20ec9811-89c5-454e-b9ed-c284f19565e4,
Identity:temporal-cli:masonegger@Masons-Laptop,
FirstExecutionRunId:20ec9811-89c5-454e-b9ed-c284f19565e4,
Attempt:1, FirstWorkflowTaskBackoff:0s,
ParentInitiatedEventVersion:0, WorkflowId:test}
2 2023-11-08T19:46:20Z WorkflowTaskScheduled {TaskQueue:{Name:backgroundcheck-replay-task-queue-local,
Kind:Normal}, StartToCloseTimeout:10s, Attempt:1}
3 2023-11-08T19:46:20Z WorkflowTaskStarted {ScheduledEventId:2,
Identity:78702@Masons-Laptop,
RequestId:1c9363fe-cc56-4a01-a91c-99337e53b792,
SuggestContinueAsNew:false,
HistorySizeBytes:680}
4 2023-11-08T19:46:20Z WorkflowTaskCompleted {ScheduledEventId:2, StartedEventId:3,
Identity:78702@Masons-Laptop,
WorkerVersion:{UseVersioning:false},
MeteringMetadata:{NonfirstLocalActivityExecutionAttempts:0}}
5 2023-11-08T19:46:20Z TimerStarted {TimerId:3fa5f3b4-3739-38a8-8ec1-1cae375321c0,
StartToFireTimeout:1m0s,
WorkflowTaskCompletedEventId:4}
6 2023-11-08T19:47:20Z TimerFired {TimerId:3fa5f3b4-3739-38a8-8ec1-1cae375321c0,
StartedEventId:5}
7 2023-11-08T19:47:20Z WorkflowTaskScheduled {TaskQueue:{Name:78702@Masons-Laptop:b5f929e5-0ef1-481f-8b79-8e0fc94c27fe,
Kind:Sticky, NormalName:backgroundcheck-replay-task-queue-local},
StartToCloseTimeout:10s, Attempt:1}
8 2023-11-08T19:47:20Z WorkflowTaskStarted {ScheduledEventId:7,
Identity:79209@Masons-Laptop,
RequestId:482675a8-8e31-4f05-b1c7-4327649c7fc4,
SuggestContinueAsNew:false,
HistorySizeBytes:1098}
9 2023-11-08T19:47:20Z WorkflowTaskFailed {ScheduledEventId:7, StartedEventId:8, Cause:NonDeterministicError, Failure:{Message:Failure handling event 5 of
type 'EVENT_TYPE_TIMER_STARTED' during replay. Event 5 of type EVENT_TYPE_TIMER_STARTED does not match command
type COMMAND_TYPE_SCHEDULE_ACTIVITY_TASK. {WorkflowTaskStartedEventId=8, CurrentStartedEventId=3}, Source:JavaSDK,
StackTrace:io.temporal.internal.statemachines.WorkflowStateMachines.handleCommandEvent(WorkflowStateMachines.java:442)
io.temporal. internal.statemachines.WorkflowStateMachines.handleSingleEvent(WorkflowStateMachines.java:346)
io.temporal.internal.stat emachines. ... skExecutor.java:105)
java.base/java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor.runWorker(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:1144)
java.base /java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor$Worker.run(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:642)
java.base/java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.j ava:1623) ,
FailureInfo:{ApplicationFailureInfo:{Type:io.temporal.worker.NonDeterministicException, NonRetryable:false}}},
Identity:79209@Masons-Laptop, ForkEventVersion:0}