Execution debugging - Temporal Nexus
Temporal Nexus is now Generally Available for Temporal Cloud and self-hosted deployments.
Nexus supports end-to-end execution debugging that may span:
- Caller Workflows
- One or more Nexus Operations executed within and across Namespaces
- Underlying Temporal primitives, like a Workflow, created by a Nexus Operation handler
This includes multi-level Nexus calls, for example:
- Workflow A → Nexus Operation 1 → Workflow B → Nexus Operation 2 → Workflow C
Bi-directional linking
Bi-directional links enable navigation of an end-to-end execution across Namespace boundaries in the Temporal UI. They are automatically added by the Temporal SDK for builder functions like New-Workflow-Run-Operation. Links are auto-wired from a specific Nexus Operation event in the caller's Workflow history to a specific event in the handler's Workflow history.
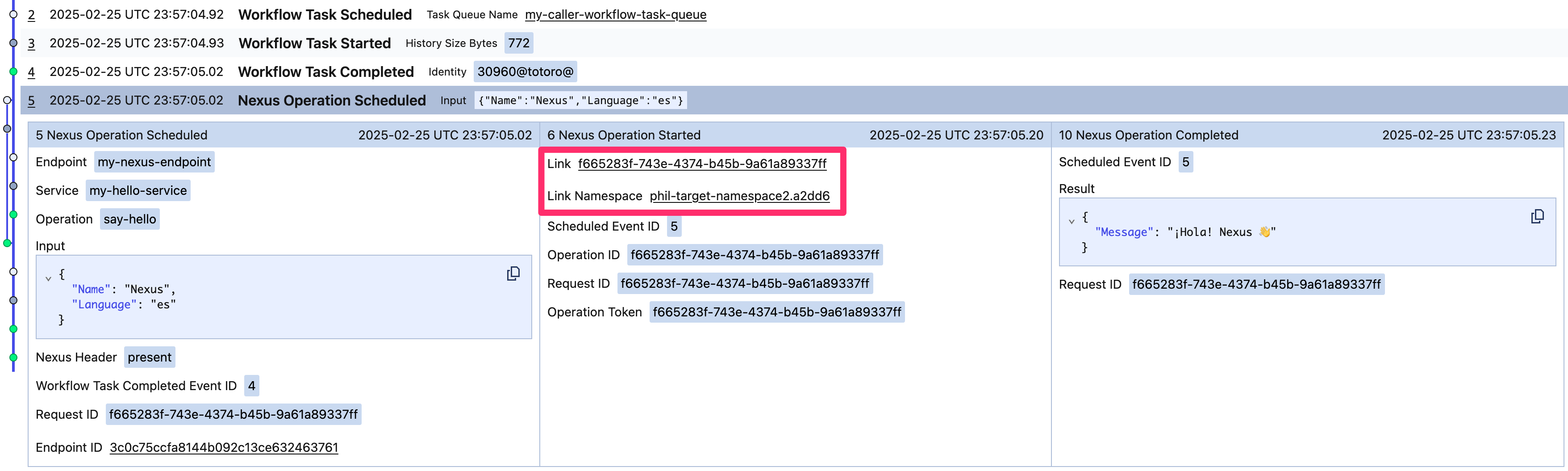
Bi-directional linking
Bi-directional links enable navigating across Namespace boundaries:
- Forward through the Nexus Operation execution:
- From a Nexus Operation event in the caller's Workflow history.
- To the underlying event in the handler's Workflow.
- Backwards through the Nexus Operation execution:
- From the underlying event in the handler's Workflow.
- To a Nexus Operation event in the caller's Workflow history.
Pending Operations
Similar to pending Activities, pending Nexus Operations are displayed in the Workflow details page and using: temporal workflow describe.
For example, from the Temporal UI:
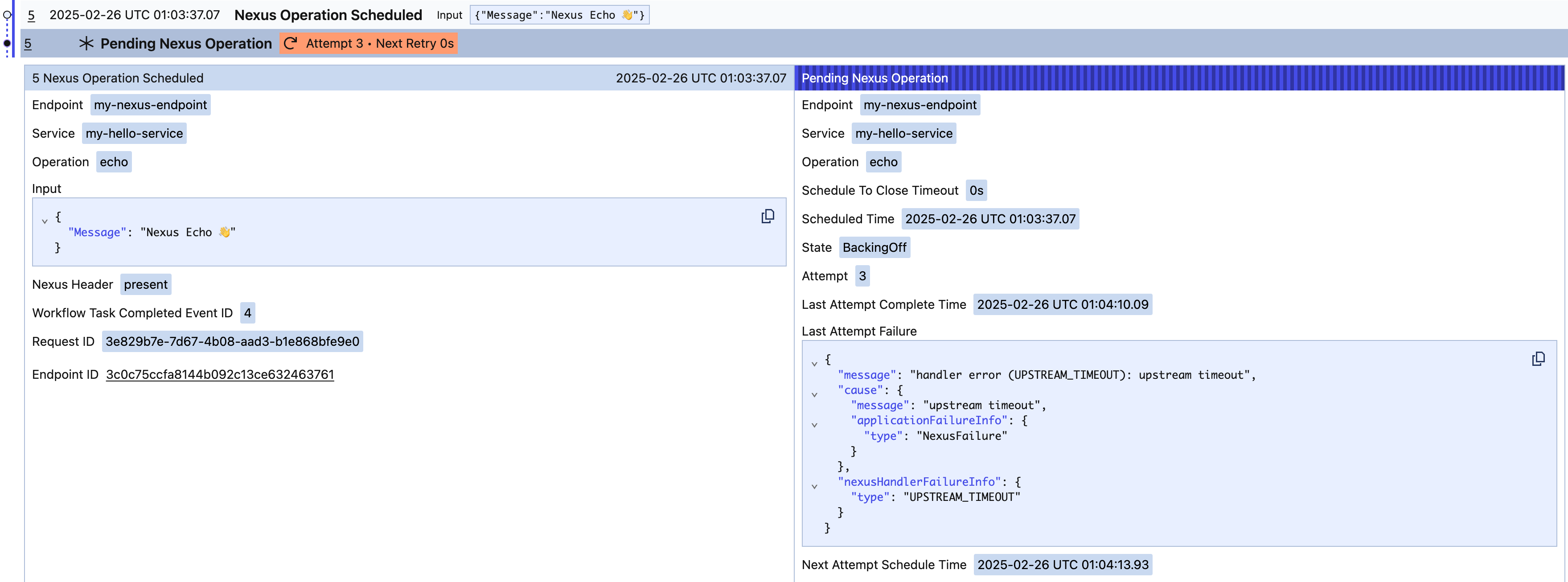
Pending Operations
For example, from the temporal CLI:
temporal workflow describe
Pending Nexus Operations: 1
Endpoint myendpoint
Service my-hello-service
Operation echo
OperationToken
State BackingOff
Attempt 6
ScheduleToCloseTimeout 0s
NextAttemptScheduleTime 20 seconds from now
LastAttemptCompleteTime 11 seconds ago
LastAttemptFailure {"message":"handler error (INTERNAL): internal error","applicationFailureInfo":{}}
Retryable Nexus errors returned from a Nexus handler will surface as part of the Pending Operation in a caller Workflow. Non-retryable errors will result in the Nexus Operation reaching a final state in the caller Workflow, with a Failed, TimedOut or Canceled event.
Pending Callbacks
Nexus callbacks are sent from the handler's Namespace to the caller's Namespace to complete an asynchronous Nexus Operation.
These show up in the UI and using: temporal workflow describe.
For example, from the Temporal UI:
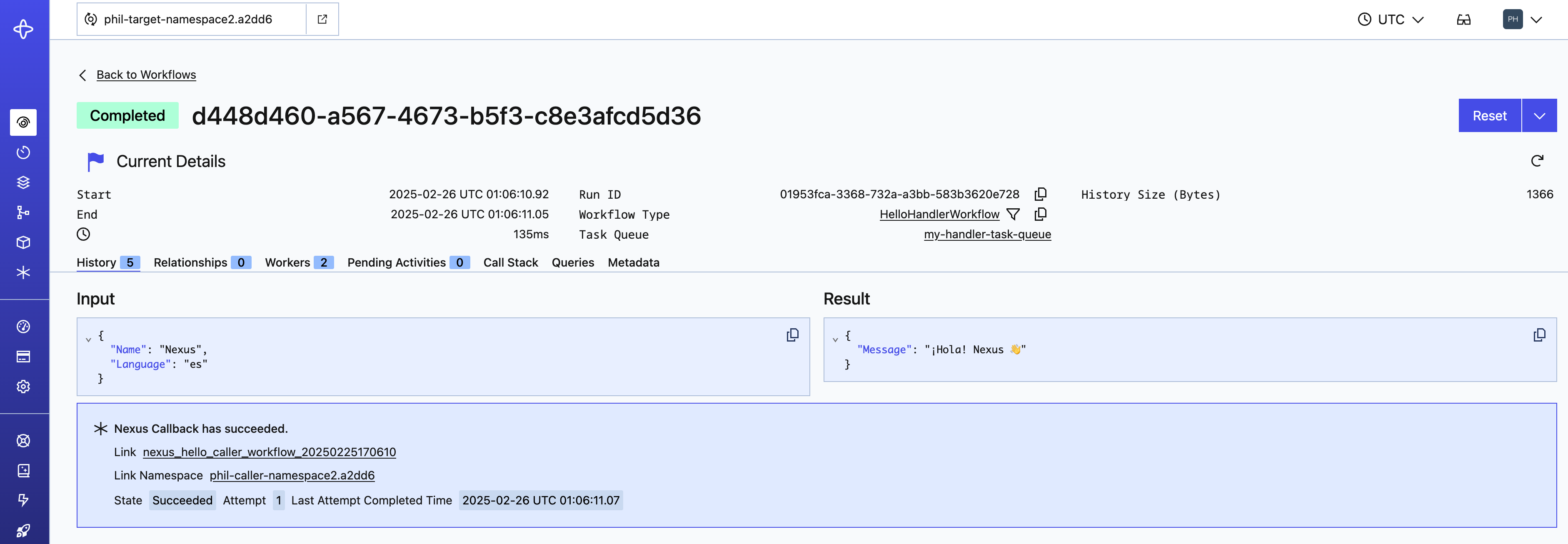
Pending Callbacks
For example, from the temporal CLI:
temporal workflow describe
Callbacks: 1
URL https://nexus.phil-caller-Namespace.a2dd6.cluster.tmprl.cloud:7243/Namespaces/phil-caller-Namespace.a2dd6/nexus/callback
Trigger WorkflowClosed
State Succeeded
Attempt 1
RegistrationTime 32 minutes ago
Tracing
Temporal integrates with tracing libraries like OpenTelemetry and OpenTracing. Tracing allows you to visualize the call graph of a Workflow, including its Activities, Nexus Operations, and Child Workflows. You can enable tracing by installing an interceptor on the Temporal Client or Worker in the supported SDKs. See the samples linked below to enable tracing for the SDKs: